How we overload our body with toxics
Each day, every day, and all through the night, your organs of detoxification are designed to collect the waste products sent them from every cell, transform them into something less toxic, and ultimately eliminate these from the body.
IMPORTANT: this system was designed to handle waste produced by your body. It was designed to inactivate and balance hormones. It was NOT designed to handle the 85,000 chemicals in use every day to kill bugs, stomp out weeds, clean and moisturize skin… hair…, wash laundry… preserve furniture, repel pests…
What is “Oxidative Stress,” and how do antioxidants fit in?
Free radicals ultimately harm and age the body. Free radicals damage DNA, the membranes of all your cells, fats… free radicals slow your ability to produce energy (chronic fatigue). A build-up of free radicals also causes arterial plaque formation and heart disease.
Normally, free radicals — or as they’re also commonly referred to, reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species — are neutralized by anti-oxidants. When this balance is disturbed, free radicals accumulated and accelerated aging occurs.
The damage done by free radicals in the body is known as “oxidation”:
- Oxidation is the same process that browns an apple or rusts metal. Rampaging free radicals react and “rust” other compounds in the body. The amount of oxidation in the body is a measure of oxidative stress.
- High levels of oxidative stress affect every organ and system in the body and have been linked with everything from Alzheimer’s disease, arteriosclerosis, cancer and heart disease to accelerated aging, asthma, diabetes and leaky gut syndrome.
- Unquenched oxidation damages cells, muscles, tissue, organs, etc.
Why do we have too many free radicals? Diets high in sugars and starches as the main source of fuel; chemicals and pesticides and preservatives and colors and… not enough antioxidant foods (vegetables and fruits—please do not try to get your antioxidants from synthetic supplements to make up for habits, it doesn’t work).
“Antioxidants” neutralize free radicals. They’re essentially “self-sacrificing soldiers” that become the reactive group instead of your cells, fats, proteins, and etc. They work everywhere, in all your cells, in your blood vessels, liver, lungs, intestines, brain…
When our enzymes of detoxification become depleted they can’t do their regular housekeeping:
 Your liver is your best friend with over 400 functions including managing toxic overload—it’s not really supposed to be managing toxic overload and will stop being able to without the right tools.
Your liver is your best friend with over 400 functions including managing toxic overload—it’s not really supposed to be managing toxic overload and will stop being able to without the right tools.
If antioxidants are lacking and toxin exposure is high, handling toxic chemicals becomes dangerous.
For example, Joe drinks a bunch of alcohol. The next morning, Joe tries to kill the hangover headache with Tylenol—which uses the same liver system: a system known as “cytochrome p450” which is an enzyme family that is supposed to be available for normal housekeeping. Instead of doing its normal housekeeping, this enzyme system now has to deal with the alcohol and Tylenol toxicity—there’s the overload.
Since 1955, we’ve known about remarkable enzymes that work in your service to get rid of your body’s toxic waste. Discovered by Axelrod and Brody, these enzymes grabbed scientific attention because they absorb light in visible spectrum (450 nm). We now know them as the cytochrome p450 enzymes.
Meet your “Phase 1” detox pathway
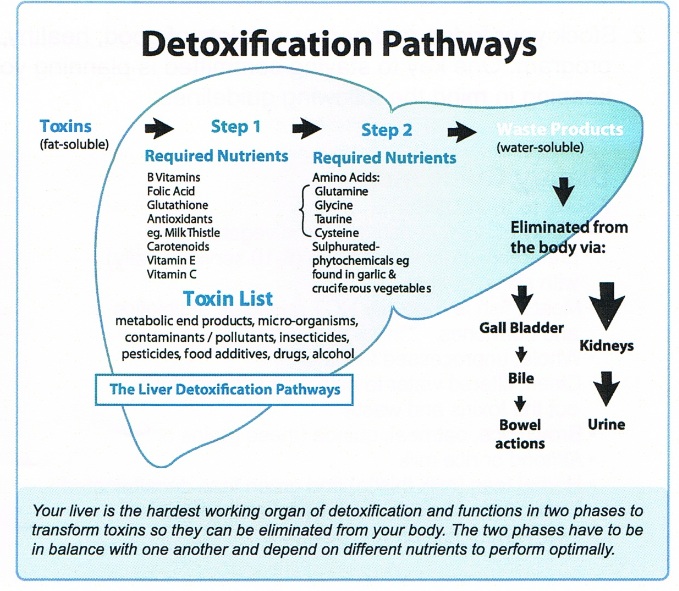
Within the liver there are two steps, or phases, of detoxification. Phase 1 takes place inside each liver cell (and a few others) by changing the chemical into something else.
The problem with this pathway is that it produces free radicals. A “free radical” is chemically very reactive; they are unstable molecules and always looking for another molecule to chemically join and stabilize themselves. Joining with another molecule is natural, and normal, and the whole point of this first step.
BUT it needs to occur in low amounts that are easily neutralized… in phase 2.
It is NOT natural or normal to have large amounts of toxics to transform, leading to large amounts of free radicals that somehow have to be neutralized.
Biochemical names aside, to put it simply:
- The p450 step converts a toxic chemical into a more harmful, more reactive chemical because it makes them into a free radical as the FIRST step in complete detoxification. A FIRST step in a series to transform the toxic waste into something the body more easily eliminates.
- During Phase 1, the body neutralizes free radical damage using antioxidants (vitamin C and E and natural carotenoids).
The problem is when the Phase I detoxification (the p450 step) exceeds the ability to neutralize.
To make things worse, Joe doesn’t eat lots of green veggies and other nutrient dense foods which contain the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants the body needs to keep the p450s working and the free radical damage neutralized. Oxidation soars and the inside of Joe begins to “rust”.
The air we breathe, the food we eat, the lotions we lather on our skin… scientists estimate the average adult has about 700 contaminants in their body at any given point.
This toxicity overloads our systems. Although the few chemicals actually tested are usually tested as carcinogens, an overload of toxicity can be the reason you can’t loose weight, have no energy, and even have sugar cravings or diabetes.
Aging also decreases blood flow through the liver. Lack of physical activity combined with poor nutrition all add up to impairment of our capacity to detoxify.
When phase 1 is faster than phase 2, liver cells are damaged and die.
Meet your “Phase 2” detox pathway
Also called the “conjugation pathway” (“conjugate” means “to join“), your liver cells add another substance (e.g. glutathione or amino acids) to the toxic chemical or drug, to render it less harmful. This also makes the toxin or drug water-soluble (can dissolve better in water), so it can then be eliminated more easily via your kidneys or intestines. Through conjugation, the liver turns drugs, hormones and various toxins into water dissolvable substances and gets rid of them.
The problem of fasting
One day, Joe decides he needs to handle his health and decides to fast.
And Joe wants to lose weight so he’s happy his fast has fewer calories (sigh. The cut calories weight loss myth is so ubiquitous).
The problems:
- When we eat greatly fewer calories, the body slows down—to conserve fuel, we go into an “energy slump.”
- To provide fuel, the body will begin to release stores of fat. On the surface this is a good thing, but…
The worst of the toxic chemicals store in fat, many of them for decades. These are now being released and need to be transformed and eliminated.
The real question is: how well-nourished was the Joe before he started his fast? Where will the antioxidants, B vitamins, proteins, glutathione, magnesium… more… where will Joe’s body get the resources to transform and eliminate these built-up toxics?
He won’t. In fact, he may feel quite sick.
Please don’t fast unless you have built up a stockpile of nutrients by eating clean for some time.
Eggs and cruciferous vegetables (e.g. broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower), raw garlic, onions, leeks and shallots are all good sources of natural compounds that enhance phase two detoxification while also providing antioxidants to quench an free radicals made by phase one. These foods and others help your liver with its cleansing actions.
The person who is not eating many of the above on a routine basis (daily, at least) should be asking: Is there a step I should take before I can safely detoxify?
The answer is. YES, you should first establish good nutrient status. Your liver needs genuine resources to do its job. And if you just switch to a clean eating lifestyle, you may have no need or desire to fast.
You don’t have to fear toxins and you don’t have to avoid smart detoxification regimens (based on whole foods and with zero boxes of supplements). Awareness, prevention and knowledge and are powerful tools. You can come clean in our toxic world.
Easy tips to reduce your toxic load:
 When it makes sense, choose organic. On a budget? If it’s the “Dirty Dozen” invest in organic; if the “Clean 15” save the money: Organically-grown food has an advantage compared to conventionally grown food in that you get far more nourishment and far fewer pesticides, insecticides, and herbicides, both on and throughout the final food.
When it makes sense, choose organic. On a budget? If it’s the “Dirty Dozen” invest in organic; if the “Clean 15” save the money: Organically-grown food has an advantage compared to conventionally grown food in that you get far more nourishment and far fewer pesticides, insecticides, and herbicides, both on and throughout the final food.
Not only that, but organic farms tend to be smaller and more sustainably run keeping their environmental impact minimal. Large commercial fields of a single crop are just as environmentally destructive and polluting as many major industries.
Drink pure, filtered or spring water. You need a lot of fluids to flush transformed toxic waste out, But drinking water contaminated with chlorine, fluoride, having residual medicines, and all the other additives and toxic chemicals just adds another burden.
Handy? Install this under-sink 3-filter system that also removes fluoride
Looking for simple? This counter-top filter has 7-stages including fluoride removal
Most of your chlorine problem comes from taking a hot shower in chlorinated water. When you shower in hot water, you inhale the steam – water vapor that contains chlorine, disinfection byproducts like trihalomethanes, and many other water pollutants.
- Filter your shower water. Get the chlorine out.
- Use “bath balls” in your amazing Epsom salt soak (which helps with magnesium—most people with a buildup of toxic chemicals are magnesium deficient)
Read the labels on your personal care products and/or look up the data in the Skin Deep database: Women “consume” some 126 chemicals from personal care products daily, and men take in 85 unique chemicals. It is essential to read your product labels like you would your food labels to avoid endocrine-disrupting chemicals such as phthalates and parabens. But even if you do, realize that cosmetic companies don’t have to list everything on the label. Anything under 5% of the total ingredients does not have to be listed (think about hormones that act at levels below 0.00000000000001%).
Make your own non-toxic products and save money to boot.
What separates a well-designed detoxification regimen from a “fad” detoxification program?
Characteristics of a safe metabolic detoxification program should include the following:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits that are organic
- Adequate calories and nutrient intake to prevent under nutrition
- Foods that are free of common food allergens such as gluten (from grains), soy… and above all sugar
- Elimination of stimulants, synthetic chemicals, alcohol, tobacco products and modified food ingredients
- Adequate amounts of fluid intake as pure water, no flavors, no additives
- Moderate amounts of exercise and movement
- Adequate fiber to promote proper bowel function and prevent constipation (plants – NOT bran)
- Adequate (but not excessive) protein, with an emphasis on sources that provide nondenatured whey to give glutathione for the conjugation pathway
- Intake of specific nutrients that have been found to support proper detoxification function, including epigallocatechin gallate from green tea, glucosinolates from cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, brussel sprouts, and cabbage).
For a safe and effective whole foods cleanse, join the next Rejuveo Guided Cleanse.
Or call me for your personalized care plan. 907-222-1824
References
Axelrod J. The enzymatic demethylation of ephedrine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1955;114, 430-438
Brody B, Axelrod J, and Cooper JR et al., Detoxification of drugs and other foreign compounds by microsomes. Science 1955;121, 603-604


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.